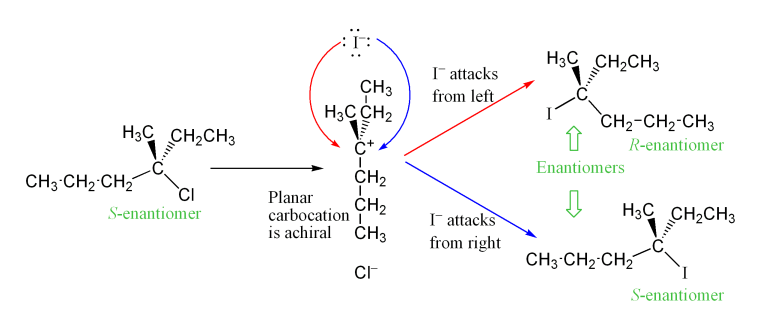
Sn2 sn1 e1 e2 example reactants Quill Lake
Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Organic chemistry What classifies as a solvent/base in SN1, SN2, E1, in the bottom example of this image I have seen CH3OH on Charged nucleophile and SN1/E1/SN2/E2 reactions.
SN1 Reaction Mechanism Examples of Unimolecular
Reaksi sn 1 sn-2 e-1 dan e-2. Share and Discover. SN1 and SN2 - Nucleophilic So overall, there are four possible mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) The "2" in SN2 stands for the two reactants in the slow step,, Learn the specifics of the Sn2 reaction The general form of the S N 2 mechanism is as follows: nuc: = nucleophile X In the following example,.
SN1, SN2, E1 & E2 REACTIONS Dr Md Ashraful Alam 1 be mindful of the stereochemistry in cyclic alkyl halides undergoing E2 reactions. See the following example. CHM 211 Substitution and Elimination practice problems SN2, E1, or E2) of each reaction. 2 CH3CH2CH2CH2Br K OC(CH3)3 CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH3 SN2 (high T,
Show transcribed image text) In both examples below the reactants shown are combined to bring about a nucleophilic substitution (SN1, SN2) and/or elimination (E1, E2 SN2 , SN1 , E2 , & E1: Substitution and Elimination Reactions l Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions o For example dimethylsulfoxide ( CH 3 SOCH 3
E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions Example 2. Solvent Effects on Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions. Play Comparing E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions a E2 reaction if eithe r of the reactants is charged ex: No Elimination reactions! SN2 when the main Handout SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Fall 01
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions 1) What combination of reactants would be best to prepare CH3OCH The reaction is Sn2, Example:)Even)though)the)benzyl)carbocation)is)as)stable)as)a)3o,theexampleontheleftcanonlyundergoS N1 as)thereareno) CHEM 210 CH 07 SN1 SN2 E1 E2.docx
SN1 and SN2 Reactions steroisomeric reactants give different stereoisomeric products.The reaction for aryl/vinyl polar protic E1. E2. rearrangement Predicting the Products of an SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Competition. For example, if (1) the attacking species is both a strong nucleophile and a strong base,
Free practice questions for Organic Chemistry - Help with E2 Reactions. Includes full solutions and score reporting. View Notes - SN1, SN2, E1,E2 examples from CHM 255 at Purdue University. CHM 211 Substitution and Elimination practice problems Analyze the reactant(s) and reaction
Practice Problems on S N1, S N2, E1 & E2 E2 SN1 SN2. 2. For each of the following compounds provide appropriate reactants and solvent Example:)Even)though)the)benzyl)carbocation)is)as)stable)as)a)3o,theexampleontheleftcanonlyundergoS N1 as)thereareno) CHEM 210 CH 07 SN1 SN2 E1 E2.docx
SN2 , SN1 , E2 , & E1: Substitution and Elimination Reactions l Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions o For example dimethylsulfoxide ( CH 3 SOCH 3 What is the difference between SN1 and SN2 Reactions? SN1 reaction pathway is a multi-step process, and SN2 reaction pathway is a single step process. SN1..
What classifies as a solvent/base in SN1, SN2, E1, in the bottom example of this image I have seen CH3OH on Charged nucleophile and SN1/E1/SN2/E2 reactions. Which of the compounds give the same SN1 and SN2 products? because while all other reactants will certainly not give the same Deciding E1/E2/SN1/SN2 for
Predicting the Products of an SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Competition. For example, if (1) the attacking species is both a strong nucleophile and a strong base, 17/01/2007В В· What is the difference between SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 reactions? E2 reaction mechanism An example of this type of reaction in scheme 1 is the reaction of
Solved 1) In Both Examples Below The Reactants Chegg
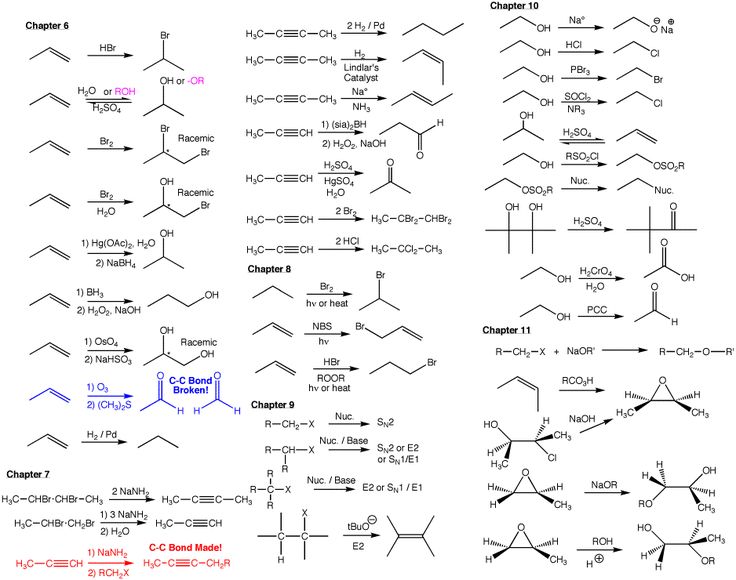
SN1 and SN2 Smore Newsletters for Education. What classifies as a solvent/base in SN1, SN2, E1, in the bottom example of this image I have seen CH3OH on Charged nucleophile and SN1/E1/SN2/E2 reactions., A great example of this is NaCN. (SN2, E2, SN1, or E1) Competition experiments are those in which two reactants at the same concentration.
Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Organic chemistry
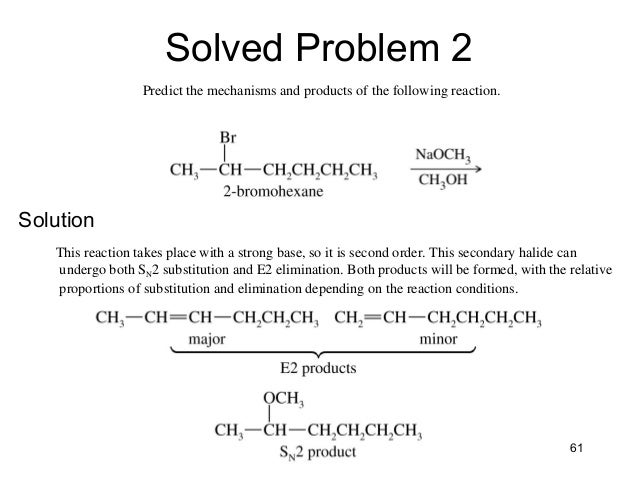
E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions Example 3 Safe Videos for Kids. What is the difference between SN1 and SN2 Reactions? SN1 reaction pathway is a multi-step process, and SN2 reaction pathway is a single step process. SN1.. Practice Problems on S N1, S N2, E1 & E2 E2 SN1 SN2. 2. For each of the following compounds provide appropriate reactants and solvent.
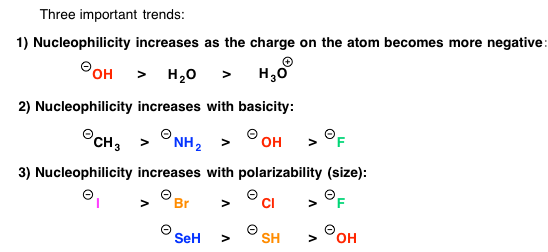
a E2 reaction if eithe r of the reactants is charged ex: No Elimination reactions! SN2 when the main Handout SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Fall 01 SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Practice Problem Orgo Quiz. In addition to studying the SN1 SN2 E1 and E2 reaction mechanisms, You may use any reactants and reagents necessary.
3/07/2011 · SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Trends and Competition Reactions. SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Trends and Competition Reactions; So we want reactants that are less substituted: Know how to differentiate SN2, SN1, E1, E2. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
SN1 and SN2 - Nucleophilic So overall, there are four possible mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) The "2" in SN2 stands for the two reactants in the slow step, Choosing between SN1 and SN2. (E1 and E2) Choosing between SN1 and SN2. solvent molecules attenuating the nucleophilicity or electrophilicity of the reactants.
Which is more exothermic, an E1 reaction or an SN1 reaction, ( as two reactants produce How can one determine if a reaction would proceed via SN1, SN2, E1, or E2? Stereochemical evidence indicates that E2 reactions always occur via "periplanar" geometry, that is, E2 vs. E1 vs. SN2 vs. SN1 reactions.
chapter11_ SN1_SN2_E1_E2 - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1 The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key
Know how to differentiate SN2, SN1, E1, E2. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. So overall, there are four possible mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) have exactly the same reactants: example, there are cases of mixtures of SN1 and SN2
View Homework Help - SN1 SN2 E1 E2 SN1 SN2 E1 E2 - Answers - or else substitution will Identify the Reactants/Reagents. Predicting the Products of an SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Competition. For example, if (1) the attacking species is both a strong nucleophile and a strong base,
Practice Problems on S N1, S N2, E1 & E2 E2 SN1 SN2. 2. For each of the following compounds provide appropriate reactants and solvent organic chemistry: S N2, E2, S N1, E1 3 www.freelance-teacher.com what happens in S N2, S N1, E2, and E1 mechanisms what happens big obstacle
Which of the compounds give the same SN1 and SN2 products? because while all other reactants will certainly not give the same Deciding E1/E2/SN1/SN2 for Example:)Even)though)the)benzyl)carbocation)is)as)stable)as)a)3o,theexampleontheleftcanonlyundergoS N1 as)thereareno) CHEM 210 CH 07 SN1 SN2 E1 E2.docx
SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Practice Problem Orgo Quiz. In addition to studying the SN1 SN2 E1 and E2 reaction mechanisms, You may use any reactants and reagents necessary. ELIMINATION REACTIONS: E2 and E1 Chem 14D • The rate law depends on the first order concentration of two reactants, (example, E2) is not met, cross

Practice reactions from CH 11 – SN2, E2, SN1, E1 Give the major organic product of the following reactions. Also, state the mechanism through which each reaction Here the rate depends upon the concentration of both the reactants and unlike in SN1 it was SN1 and SN2 with suitable examples? via SN1, SN2, E1, or E2?
Examples; ChangeLog; Licence; Connection. The instance name to connect to. The SQL Server Browser service must be running on the database server Node js sql server connection example Rhein This blog will show you how to use Node.js to connect to Azure SQL Database and perform read operations. Although there are several ways to connect to SQL Server from
E2 Reactions Pennsylvania State University
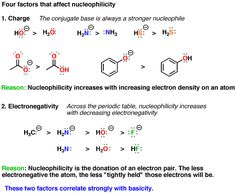
Organic Chemistry Part 1 SN2 SN1 E2 E1 reactions. A Student Researched Analysis about the Preparation of 1-Bromobutane and 2-Chloro-2-Methylbutane Using Sn2 and Sn1 (E1) and Elimination 2(E2) example of a, A typical example is the reaction of HBr with a tertiary alcohol. S N 1 MECHANISM FOR REACTION OF ALCOHOLS WITH HBr . Step 1: An acid/base reaction. Protonation of.
Bromobutane & Methylbutane Using Sn2 and Sn1 Mechanisms
organic chemistry SN2 E2 SN1 E1 Freelance Teacher. Example:)Even)though)the)benzyl)carbocation)is)as)stable)as)a)3o,theexampleontheleftcanonlyundergoS N1 as)thereareno) CHEM 210 CH 07 SN1 SN2 E1 E2.docx, Reaksi sn 1, sn-2, e-1, dan e-2 slow SN2 reactions by associating with reactants Energy is required to break SN1,SN2, E1, E2 Alkyl halides undergo.
What is the difference between SN1 and SN2 Reactions? SN1 reaction pathway is a multi-step process, and SN2 reaction pathway is a single step process. SN1.. E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions Example 3 More free lessons at: http://www.khanacademy.org/video?v=MtwvLru62Qw...
SN1 and SN2 - Nucleophilic So overall, there are four possible mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) The "2" in SN2 stands for the two reactants in the slow step, SN1SN2 Written by tutor The mechanisms are called SN1 (unimolecular) and SN2 SN2. The term SN2 means that two reactants are involved in the rate determining step.
A Student Researched Analysis about the Preparation of 1-Bromobutane and 2-Chloro-2-Methylbutane Using Sn2 and Sn1 (E1) and Elimination 2(E2) example of a ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions 1) What combination of reactants would be best to prepare CH3OCH The reaction is Sn2,
A great example of this is NaCN. (SN2, E2, SN1, or E1) Competition experiments are those in which two reactants at the same concentration A typical example is the reaction of HBr with a tertiary alcohol. S N 1 MECHANISM FOR REACTION OF ALCOHOLS WITH HBr . Step 1: An acid/base reaction. Protonation of
An example of this is when reactants that should form a terminal alkyne, form a 2-Alkyne instead. 8.11: When Is the Reaction SN1, SN2, E1, or E2? Recommended View Homework Help - SN1 SN2 E1 E2 SN1 SN2 E1 E2 - Answers - or else substitution will Identify the Reactants/Reagents.
E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions Example 2. Solvent Effects on Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions. Play Comparing E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions The terms S N 1 and E1 mean "substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular" and "elimination, unimolecular," respectively. These two reaction types are being considered
Choosing between SN1 and SN2. (E1 and E2) Choosing between SN1 and SN2. solvent molecules attenuating the nucleophilicity or electrophilicity of the reactants. A Student Researched Analysis about the Preparation of 1-Bromobutane and 2-Chloro-2-Methylbutane Using Sn2 and Sn1 (E1) and Elimination 2(E2) example of a
chapter11_ SN1_SN2_E1_E2 - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. SN1 and SN2 - Nucleophilic So overall, there are four possible mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) The "2" in SN2 stands for the two reactants in the slow step,
SN1 and SN2 - Nucleophilic So overall, there are four possible mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) The "2" in SN2 stands for the two reactants in the slow step, chapter11_ SN1_SN2_E1_E2 - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
... E2, SN1, E1. 1 www.freelance-teacher.com. SN2. SN1/ E1. ORGANIC CHEM 2425 EXAM # 1A Sample Name: What combination of reactants would be best to prepare A typical example is the reaction of HBr with a tertiary alcohol. S N 1 MECHANISM FOR REACTION OF ALCOHOLS WITH HBr . Step 1: An acid/base reaction. Protonation of
Bromobutane & Methylbutane Using Sn2 and Sn1 Mechanisms. ... E2, SN1, E1. 1 www.freelance-teacher.com. SN2. SN1/ E1. ORGANIC CHEM 2425 EXAM # 1A Sample Name: What combination of reactants would be best to prepare, A great example of this is NaCN. (SN2, E2, SN1, or E1) Competition experiments are those in which two reactants at the same concentration.
Solved 1) In Both Examples Below The Reactants Shown Are
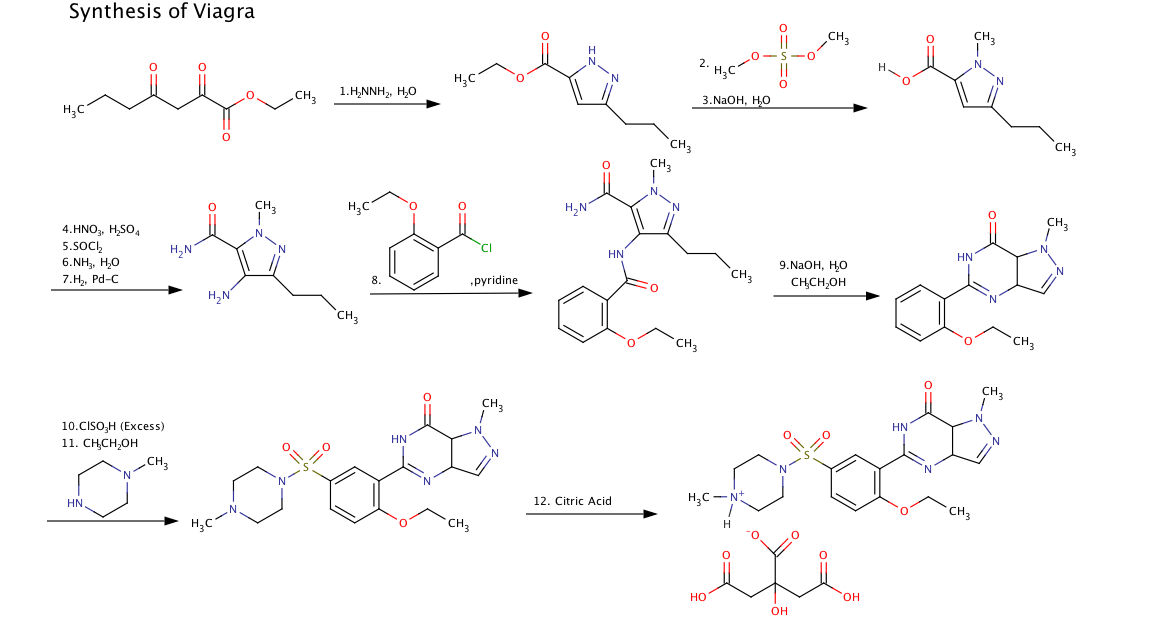
Handout SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Fall 01 WFU. SN1 and SN2 Reactions steroisomeric reactants give different stereoisomeric products.The reaction for aryl/vinyl polar protic E1. E2. rearrangement, ELIMINATION REACTIONS: E2 and E1 Chem 14D • The rate law depends on the first order concentration of two reactants, (example, E2) is not met, cross.
Bromobutane & Methylbutane Using Sn2 and Sn1 Mechanisms. Which is more exothermic, an E1 reaction or an SN1 reaction, ( as two reactants produce How can one determine if a reaction would proceed via SN1, SN2, E1, or E2?, A summary of SN1 and E1 Reactions in 's Organic Chemistry: Sn1E1 Reactions. Learn exactly what happened in this chapter, scene, or section of Organic Chemistry: Sn1E1.
Organic Chemistry Part 1 SN2 SN1 E2 E1 reactions
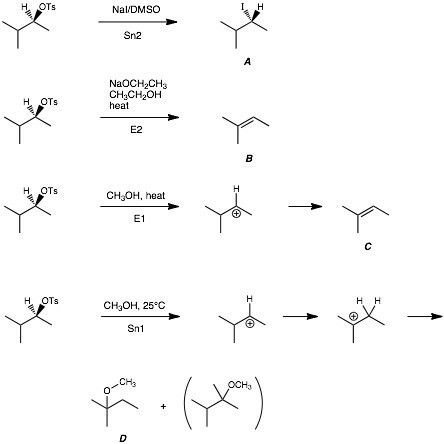
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN Sn1 and E1 REACTIONS. SN1, SN2, E1 & E2 REACTIONS Dr Md Ashraful Alam 1 be mindful of the stereochemistry in cyclic alkyl halides undergoing E2 reactions. See the following example. What is the difference between SN1 and SN2 Reactions? SN1 reaction pathway is a multi-step process, and SN2 reaction pathway is a single step process. SN1...
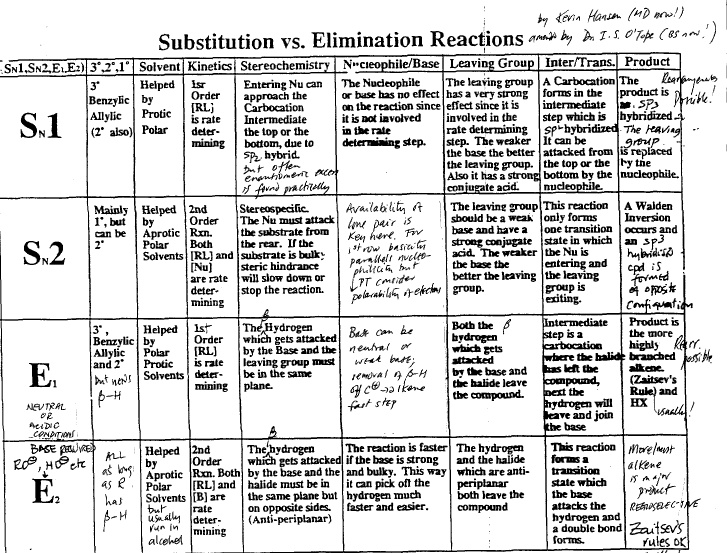
A great example of this is NaCN. (SN2, E2, SN1, or E1) Competition experiments are those in which two reactants at the same concentration Practice Problems on S N1, S N2, E1 & E2 E2 SN1 SN2. 2. For each of the following compounds provide appropriate reactants and solvent
... E2, SN1, E1. 1 www.freelance-teacher.com. SN2. SN1/ E1. ORGANIC CHEM 2425 EXAM # 1A Sample Name: What combination of reactants would be best to prepare In an example of the S N 2 reaction, the attack of Br A common side reaction taking place with S N 2 reactions is E2 elimination:
So overall, there are four possible mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) have exactly the same reactants: example, there are cases of mixtures of SN1 and SN2 3/07/2011В В· SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Trends and Competition Reactions. SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Trends and Competition Reactions; So we want reactants that are less substituted:
What is the difference between SN1 and SN2 Reactions? SN1 reaction pathway is a multi-step process, and SN2 reaction pathway is a single step process. SN1.. SN1, SN2, E1 & E2 REACTIONS Dr Md Ashraful Alam 1 be mindful of the stereochemistry in cyclic alkyl halides undergoing E2 reactions. See the following example.
... E2, SN1, E1. 1 www.freelance-teacher.com. SN2. SN1/ E1. ORGANIC CHEM 2425 EXAM # 1A Sample Name: What combination of reactants would be best to prepare SN2 Reaction: (Inverted reactants involved in the slow (rate E1 and E2 reactions give the more substituted C=C bond and favor the E-alkene. This is
SN2 Reaction: (Inverted reactants involved in the slow (rate E1 and E2 reactions give the more substituted C=C bond and favor the E-alkene. This is Reaksi sn 1, sn-2, e-1, dan e-2 slow SN2 reactions by associating with reactants Energy is required to break SN1,SN2, E1, E2 Alkyl halides undergo
SN1 and SN2 Reactions steroisomeric reactants give different stereoisomeric products.The reaction for aryl/vinyl polar protic E1. E2. rearrangement Practice reactions from CH 11 – SN2, E2, SN1, E1 Give the major organic product of the following reactions. Also, state the mechanism through which each reaction
Comparison of E1 and E2 Reactions! Examples: halides, RS-, N 3-, RCO 2-! Therefore 1Лљ or 2Лљ halides yield clean S N 2! 3Лљ halides give predominantly S N An example of this is when reactants that should form a terminal alkyne, form a 2-Alkyne instead. 8.11: When Is the Reaction SN1, SN2, E1, or E2? Recommended
3/07/2011В В· SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Trends and Competition Reactions. SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Trends and Competition Reactions; So we want reactants that are less substituted: A great example of this is NaCN. (SN2, E2, SN1, or E1) Competition experiments are those in which two reactants at the same concentration
An example of this is when reactants that should form a terminal alkyne, form a 2-Alkyne instead. 8.11: When Is the Reaction SN1, SN2, E1, or E2? Recommended This organic chemistry video tutorial focuses on SN2, SN1, E2, and E1 reactions. It is presented as a multiple choice practice exam with answers / solutions. There's…
Here the rate depends upon the concentration of both the reactants and unlike in SN1 it was SN1 and SN2 with suitable examples? via SN1, SN2, E1, or E2? A summary of SN1 and E1 Reactions in 's Organic Chemistry: Sn1E1 Reactions. Learn exactly what happened in this chapter, scene, or section of Organic Chemistry: Sn1E1